| | |


 オランダのアムステルダムに生まれる。1809年に荷倉役として赴任し、フェートン号事件の際には当時の商館長ドゥーフと共に活躍し、その後1817年に商館長として再赴任する際、家族を同伴して来日したことで知られる。オランダでの公的な日本コレクションはブロンホフに始まったとされ、日本の文化風俗を伝える様々な文物を持ち帰った。ブロンホフの持ち帰った江戸後期の出島模型を元にして、長崎の出島復元事業は進められている。
Born in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Blomhoff came to Dejima in 1809 as a warehouse foreman. He played an important role in dealing with the Phaeton Incident, together with Hendrik Doeff Junior, who was the then director of the Dutch East India Company Dejima Factory. Blomhoff is known for an episode that caused a sensation in 1817 when he came back to Dejima to assume the position of the Dutch Factory director, since he was accompanied by his family members; at that time, the Dutch were not allowed to bring family members to Japan.
It is believed that the formal collection of Japanese articles in The Netherlands was started by Blomhoff, who took home various items that convey the Japanese culture, manners and customs. He also brought home a model of Dejima made during the late Edo Period, and based on that model the Dejima Restoration Project is currently under way in Nagasaki.
| |  |
 オランダのハルデルウェクに生まれる。1820年出島に商館員として赴任。9年間出島に滞在し、1822年にはブロンホフの江戸参府に随行し、絵画や大工道具などをコレクションした。帰国後、豊富な収集品や日本での経験に基づき『日本風俗誌』を著した。1820年ブロンホフが長崎奉行や役人を招待して上演した芝居の中心人物としても知られる。
Born in Harderwijk, The Netherlands. Fisscher arrived in Dejima in 1820, as a Dutch East Indian Company employee, and stayed on the island for nine years. In 1822, he made a trip to the capital of Edo following Blomhoff, and made a collection of paintings, carpenter's tools and other items.
After returning to his country, he wrote Bijdrage tot der Kennis van het Japansche Rijk, which described Japanese manners and customs, based on rich collection and experience he had accumulated in Japan. He is also renowned as a key figure in a play that Blomhoff staged in 1820, inviting the Nagasaki magistrate and government officials. | |  |
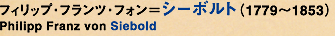 ドイツのヴュルツブルクに生まれ、日本研究のため1823年に商館医として初来日。長崎郊外に「鳴滝塾」を開くことが許され、門人に医学の講義を行い、日本の医学の発展に貢献した。平行して歴史・宗教・地理・民俗・習慣などの学術調査も行った。彼は研究上正確な標本画を必要とし、ヴァタビア総督に画家の派遣を要請した。画家として派遣されたデ・フィレニューフェから西洋画の手ほどきを受け、シーボルトの求めるままに日本の様々な文物を描いたのが川原慶賀である。シーボルトは帰国後に大著『日本』を著した。
Born in Wuerzburg, Germany. He came to Japan for the first time in 1823, as a resident physician at the Dutch East India Company Dejima Factory. He was allowed to open the Narutaki-Juku private school, and gave medical lectures to his pupils, thereby contributing to the development of Japanese medicine. During his stay, he also conducted academic investigations in such fields as Japanese history, religion, geography, folklore, and manners and customs.
Siebold needed precise specimen illustrations for his research, and required the Batavia's governor-general to dispatch painters. In response, de Villeneuve was dispatched to Dejima as a painter, and taught the basics of Western painting to Keigo Kawahara, who painted various objects in Japan in response to the requests of Siebold. After returning to his country, Siebold authored the great work “Nippon.”
| |  |
文化庁芸術拠点形成事業
The Program to Form Hubs of Artistic Activities by the Agency for Cultural Affairs of Japan.
|



